How to Write a Mouse Listener
Tracking the cursor's motion involves significantly more system overhead than tracking other mouse events. That is why mouse-motion events are separated into Mouse Motion listener type (see How to Write a Mouse Motion Listener).
To track mouse wheel events, you can register a mouse-wheel listener. See How to Write a Mouse Wheel Listener for more information.
If an application requires the detection of both mouse events
and mouse-motion events,
use the
MouseInputAdapter class. This class implements the
MouseInputListener, a convenient interface that
implements the MouseListener and
MouseMotionListener interfaces. However, the MouseInputListener interface does not implement
the MouseWheelListener interface.
Alternatively, use the corresponding AWT
MouseAdapter class, which implements the MouseListener, MouseMotionListener, and MouseWheelListener interfaces.
The following example shows a mouse listener.
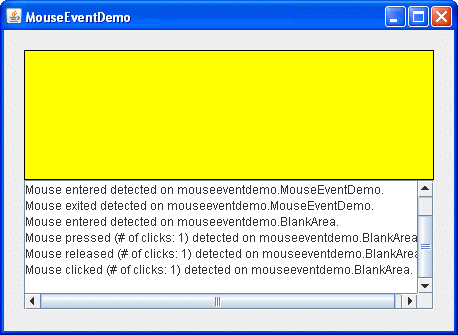
At the top of the window is a blank area
(implemented by a class named BlankArea).
The mouse listener listens for events
both on the BlankArea
and on its container,
an instance of MouseEventDemo.
Each time a mouse event occurs,
a descriptive message is displayed
under the blank area.
By moving the cursor on top of the blank area
and occasionally pressing mouse buttons,
you can fire mouse events.
Try this:
- Click the Launch button
to run MouseEventDemo using
Java™ Web Start
(download JDK 6).
Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself,
consult the
example index.

- Move the cursor into the yellow rectangle
at the top of the window.
You will see one or more mouse-entered events. - Press and hold the left mouse button without moving the mouse.
You will see a mouse-pressed event. You might see some extra mouse events, such as mouse-exited and then mouse-entered. - Release the mouse button.
You will see a mouse-released event. If you did not move the mouse, a mouse-clicked event will follow. - Press and hold the mouse button again,
and then drag the mouse so that the cursor ends up
outside the window.
Release the mouse button.
You will see a mouse-pressed event, followed by a mouse-exited event, followed by a mouse-released event. You are not notified of the cursor's motion. To get mouse-motion events, you need to implement a mouse-motion listener.
MouseEventDemo.java
and
BlankArea.java.
Here is the demo's mouse event handling code:
public class MouseEventDemo ... implements MouseListener {
//where initialization occurs:
//Register for mouse events on blankArea and the panel.
blankArea.addMouseListener(this);
addMouseListener(this);
...
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
saySomething("Mouse pressed; # of clicks: "
+ e.getClickCount(), e);
}
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {
saySomething("Mouse released; # of clicks: "
+ e.getClickCount(), e);
}
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {
saySomething("Mouse entered", e);
}
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) {
saySomething("Mouse exited", e);
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
saySomething("Mouse clicked (# of clicks: "
+ e.getClickCount() + ")", e);
}
void saySomething(String eventDescription, MouseEvent e) {
textArea.append(eventDescription + " detected on "
+ e.getComponent().getClass().getName()
+ "." + newline);
}
}
The Mouse Listener API
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| mouseClicked(MouseEvent) | Called just after the user clicks the listened-to component. |
| mouseEntered(MouseEvent) | Called just after the cursor enters the bounds of the listened-to component. |
| mouseExited(MouseEvent) | Called just after the cursor exits the bounds of the listened-to component. |
| mousePressed(MouseEvent) | Called just after the user presses a mouse button while the cursor is over the listened-to component. |
| mouseReleased(MouseEvent) | Called just after the user releases a mouse button after a mouse press over the listened-to component. |
The
MouseAdapter class (the AWT adapter class) is abstract. All its methods have an empty body. So a developer can define methods for events specific to the application. You can also use the
MouseInputAdapter class, which has all the methods available from MouseListener
and MouseMotionListener.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int getClickCount() | Returns the number of quick, consecutive clicks the user has made (including this event). For example, returns 2 for a double click. |
|
int getX() int getY() Point getPoint() |
Return the (x,y) position at which the event occurred, relative to the component that fired the event. |
|
int getXOnScreen() int getYOnScreen() int getLocationOnScreen() |
Return the absolute (x,y) position of the event. These coordinates are relative to the virtual coordinate system for the multi-screen environment. Otherwise, these coordinates are relative to the coordinate system associated with the Component's Graphics Configuration. |
| int getButton() | Returns which mouse button, if any, has a changed state. One of
the following constants is returned: NOBUTTON,
BUTTON1, BUTTON2, or BUTTON3.
Introduced in release 1.4.
|
| boolean isPopupTrigger() | Returns true if the mouse event should cause a popup menu
to appear. Because popup triggers are platform dependent,
if your program uses popup menus,
you should call isPopupTrigger
for all mouse-pressed and mouse-released events
fired by components over which the popup can appear.
See Bringing Up a Popup Menu
for more information about popup menus.
|
| String getMouseModifiersText(int) | Returns a String describing the modifier keys
and mouse buttons that were active during the event, such
as "Shift", or "Ctrl+Shift". These strings can be localized
using the awt.properties file. Introduced in release 1.4.
|
The MouseEvent class inherits many useful
methods from
InputEvent and a couple handy methods from the
ComponentEvent and
AWTEvent classes.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
int getID() (in java.awt.AWTEvent)
|
Returns the event type, which defines the particular action.
For example, the MouseEvent id reflects the state of the mouse buttons for every mouse event.
The following states could be specified by the MouseEvent id: MouseEvent.MOUSE_PRESSED, MouseEvent.MOUSE_RELEASED, and MouseEvent.MOUSE_CLICKED.
|
|
Component getComponent() (in ComponentEvent)
|
Returns the component that fired the event.
You can use this method instead of the getSource method.
|
| int getWhen() | Returns the timestamp of when this event occurred. The higher the timestamp, the more recently the event occurred. |
|
boolean isAltDown() boolean isControlDown() boolean isMetaDown() boolean isShiftDown() |
Return the state of individual modifier keys at the time the event was fired. |
| int getModifiers() | Returns the state of all the modifier keys and
mouse buttons when the event was fired.
You can use this method to determine which
mouse button was pressed (or released) when a
mouse event was fired.
The InputEvent class defines these constants
for use with the getModifiers method:
ALT_MASK,
BUTTON1_MASK,
BUTTON2_MASK,
BUTTON3_MASK,
CTRL_MASK,
META_MASK, and
SHIFT_MASK.
For example, the following expression is true
if the right button was pressed:
(mouseEvent.getModifiers() & InputEvent.BUTTON3_MASK) == InputEvent.BUTTON3_MASK |
| int getModifiersEx() | Returns the extended modifier mask for this event.
Extended modifiers represent the state of the mouse button and all modal keys,
such as ALT, CTRL, META, just after
the event occurred. You can check the status of the modifiers
using one of the following predefined bitmasks:
SHIFT_DOWN_MASK, CTRL_DOWN_MASK,
META_DOWN_MASK, ALT_DOWN_MASK,
BUTTON1_DOWN_MASK, BUTTON2_DOWN_MASK,
BUTTON3_DOWN_MASK, or ALT_GRAPH_DOWN_MASK.
For example, to check that button 1 is down,
but that buttons 2 and 3 are up, you would use the following code snippet:
if (event.getModifiersEx() & (BUTTON1_DOWN_MASK |
BUTTON2_DOWN_MASK |
BUTTON3_DOWN_MASK)
== BUTTON1_DOWN_MASK) {
...
}
|
| int getModifiersExText(int) | Returns a string describing the extended modifier keys and mouse buttons, such as "Shift", "Button1", or "Ctrl+Shift". These strings can be localized by changing the awt.properties file. Introduced in release 1.4. |
The
MouseInfo class provides methods to obtain information about the mouse pointer location
at any time while an application runs.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| getPointerInfo() |
Returns a PointerInfo instance that represents the current location of the mouse pointer.
|
| getNumberOfButtons() |
Returns the number of buttons on the mouse or -1 , if a system does not support a mouse.
|
Examples That Use Mouse Listeners
The following table lists the examples that use mouse listeners.
| Example | Where Described | Notes |
|---|---|---|
MouseEventDemo
|
This section | Reports all mouse events that occur within a blank panel to demonstrate the circumstances under which mouse events are fired. |
GlassPaneDemo
|
How to Use Root Panes | Uses a subclass of MouseInputAdapter to
listen to mouse events and mouse-motion events
on the root pane's glass pane.
Re-dispatches the events to underlying components.
|
TableSortDemo
|
How to Use Tables | Listens to mouse events on a table header. Sorts data in the selected column. |
PopupMenuDemo
|
How to Use Menus | Displays a popup menu in response to mouse clicks. |
TrackFocusDemo
|
How to Use the Focus Subsystem | The custom component, Picture,
implements a mouse listener that requests
the focus when a user clicks on the component.
|
