How to Write a Key Listener
Note: To define special reactions to particular keys, use key bindings instead of a key listener. For further information, see How to Use Key Bindings.
Notifications are sent about two basic kinds of key events:
- The typing of a Unicode character
- The pressing or releasing of a key on the keyboard
In general, you react to only key-typed events unless you need to know when the user presses keys that do not correspond to characters. For example, to know when the user types a Unicode character — whether by pressing one key such as 'a' or by pressing several keys in sequence — you handle key-typed events. On the other hand, to know when the user presses the F1 key, or whether the user pressed the '3' key on the number pad, you handle key-pressed events.
Note: To fire keyboard events, a component must have the keyboard focus.
To make a component get the keyboard focus, follow these steps:
- Make sure the component's
isFocusablemethod returnstrue. This state allows the component to receive the focus. For example, you can enable keyboard focus for aJLabelcomponent by calling thesetFocusable(true)method on the label. - Make sure the component requests the focus
when appropriate. For custom components, implement a mouse listener
that calls the
requestFocusInWindowmethod when the component is clicked.
Version note: This page reflects the focus API introduced in JDK release 1.4. As of that release, the focus subsystem consumes focus traversal keys, such as Tab and Shift Tab. If you need to prevent the focus traversal keys from being consumed, you can call
component.setFocusTraversalKeysEnabled(false)
KeyEventDispatcher class to pre-listen
to all key events. The
focus page has detailed information on the focus subsystem.
For key-typed events you can obtain the key character value as well as any modifiers used.
Note: You should not rely on the key character value returned from
getKeyChar unless it is involved in a
key-typed event.
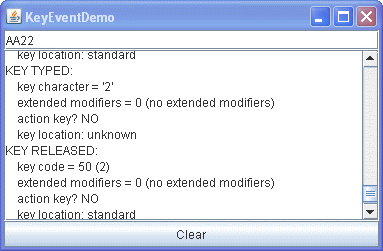
The following example demonstrates key events. It consists of a text field that you can type into, followed by a text area that displays a message every time the text field fires a key event. A button at the bottom of the window lets you clear both the text field and text area.
Try this:
- Click the Launch button
to run KeyEventDemo using
Java™ Web Start
(download JDK 6).
Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself,
consult the
example index.

- Type a lowercase 'a' by pressing and releasing
the A key on the keyboard.
The text field fires three events: a key-pressed event, a key-typed event, and a key-released event. Note that the key-typed event doesn't have key code information, and key-pressed and key-released events don't have key character information. None of the events so far are from modifier or action keys and the key location, reported on the key-pressed and key-released events, is most likely standard. - Press the Clear button.
You might want to do this after each of the following steps. - Press and release the Shift key.
The text field fires two events: a key-pressed and a key-released. The text field doesn't fire a key-typed event because Shift, by itself, doesn't correspond to any character. - Type an uppercase 'A' by pressing the Shift and A keys.
You'll see the following events, although perhaps not in this order: key-pressed (Shift), key-pressed (A), key typed ('A'), key-released (A), key-released (Shift). Note that Shift is listed as the modifier key for the key-typed and key-pressed events. - Type an uppercase 'A' by pressing and releasing
the Caps Lock key, and then pressing the A key.
You should see the following events: key-pressed (Caps Lock), key-pressed (A), key typed ('A'), key-released (A). Note that Caps Lock is not listed as a modifier key. - Press the Tab key. No Tab key-pressed or key-released events are received by the key event listener. This is because the focus subsystem consumes focus traversal keys, such as Tab and Shift Tab. Press Tab twice more to return the focus to the text area.
- Press a function key, such as F3. You'll see that the function key is an action key.
- Press the left Shift key, followed by the right Shift key. The key-pressed and key-released events indicate which Shift key was typed.
- Press the Num Lock key if your keyboard has a number pad.
As for Caps Lock, there is a key-pressed event, but no key-released event. - Press the '2' key on the number pad. You see the key-pressed, key-typed, and key-released events for the number '2'.
- Press the '2' key on the standard keyboard. Again, you see the three event messages. The key-typed events for both number 2 keys are identical. But the key-pressed and key-released events indicate different key codes and different key locations.
- Press the Num Lock key again. A key-released event is fired.
You can find the example's code in
KeyEventDemo.java.
Here is the demo's key event handling code:
public class KeyEventDemo ... implements KeyListener ... {
...//where initialization occurs:
typingArea = new JTextField(20);
typingArea.addKeyListener(this);
//Uncomment this if you wish to turn off focus
//traversal. The focus subsystem consumes
//focus traversal keys, such as Tab and Shift Tab.
//If you uncomment the following line of code, this
//disables focus traversal and the Tab events
//become available to the key event listener.
//typingArea.setFocusTraversalKeysEnabled(false);
...
/** Handle the key typed event from the text field. */
public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e) {
displayInfo(e, "KEY TYPED: ");
}
/** Handle the key-pressed event from the text field. */
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
displayInfo(e, "KEY PRESSED: ");
}
/** Handle the key-released event from the text field. */
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {
displayInfo(e, "KEY RELEASED: ");
}
...
private void displayInfo(KeyEvent e, String keyStatus){
//You should only rely on the key char if the event
//is a key typed event.
int id = e.getID();
String keyString;
if (id == KeyEvent.KEY_TYPED) {
char c = e.getKeyChar();
keyString = "key character = '" + c + "'";
} else {
int keyCode = e.getKeyCode();
keyString = "key code = " + keyCode
+ " ("
+ KeyEvent.getKeyText(keyCode)
+ ")";
}
int modifiersEx = e.getModifiersEx();
String modString = "extended modifiers = " + modifiersEx;
String tmpString = KeyEvent.getModifiersExText(modifiersEx);
if (tmpString.length() > 0) {
modString += " (" + tmpString + ")";
} else {
modString += " (no extended modifiers)";
}
String actionString = "action key? ";
if (e.isActionKey()) {
actionString += "YES";
} else {
actionString += "NO";
}
String locationString = "key location: ";
int location = e.getKeyLocation();
if (location == KeyEvent.KEY_LOCATION_STANDARD) {
locationString += "standard";
} else if (location == KeyEvent.KEY_LOCATION_LEFT) {
locationString += "left";
} else if (location == KeyEvent.KEY_LOCATION_RIGHT) {
locationString += "right";
} else if (location == KeyEvent.KEY_LOCATION_NUMPAD) {
locationString += "numpad";
} else { // (location == KeyEvent.KEY_LOCATION_UNKNOWN)
locationString += "unknown";
}
...//Display information about the KeyEvent...
}
}
The Key Listener API
The corresponding adapter class is
KeyAdapter.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| keyTyped(KeyEvent) | Called just after the user types a Unicode character into the listened-to component. |
| keyPressed(KeyEvent) | Called just after the user presses a key while the listened-to component has the focus. |
| keyReleased(KeyEvent) | Called just after the user releases a key while the listened-to component has the focus. |
The KeyEvent class inherits many useful
methods from the
InputEvent class, such as getModifiersEx, and a couple of
useful methods from the
ComponentEvent and
AWTEvent classes. See the
InputEvent Class
table in the
mouse listener page for
a complete list.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| int getKeyChar() | Obtains the Unicode character associated with this event. Only rely on this value for key-typed events. |
| int getKeyCode() | Obtains the key code associated with this event.
The key code identifies the particular key
on the keyboard that the user pressed or released.
The KeyEvent class defines many key code constants
for commonly seen keys.
For example, VK_A specifies the key labeled A,
and VK_ESCAPE specifies the Escape key.
|
|
String getKeyText(int) String getKeyModifiersText(int) |
Return text descriptions of the event's key code and modifier keys, respectively. |
|
int getModifiersEx() String getModifiersExText(int modifiers) |
Return the extended modifiers mask for this event. There are methods inherited from the InputEvent class. Extended modifiers represent the state of all modal keys.
The getModifiersExText method returns a string describing the extended modifier keys and mouse buttons.
Since the getModifiersEx and getModifiersExText methods provide more information about key events, they are preferred over the getKeyText or getKeyModifiersText methods.
|
| boolean isActionKey() | Returns true if the key firing the event is an action key. Examples of action keys include Cut, Copy, Paste, Page Up, Caps Lock, the arrow and function keys. This information is valid only for key-pressed and key-released events. |
| int getKeyLocation() | Returns the location of the key that fired this event. This
provides a way to distinguish keys that occur more than once
on a keyboard, such as the two shift keys, for example.
The possible values are KEY_LOCATION_STANDARD,
KEY_LOCATION_LEFT, KEY_LOCATION_RIGHT,
KEY_LOCATION_NUMPAD, or KEY_LOCATION_UNKNOWN.
This method always returns KEY_LOCATION_UNKNOWN for
key-typed events. Introduced in JDK release 1.4.
|
Examples that Use Key Listeners
The following table lists the examples that use key listeners.
| Example | Where Described | Notes |
|---|---|---|
KeyEventDemo
|
This section | Reports all key events that occur on a text field to demonstrate the circumstances under which key events are fired. |
