Lesson: Overview of JNDI
Architecture
The JNDI architecture consists of an API and a service provider interface (SPI). Java applications use the JNDI API to access a variety of naming and directory services. The SPI enables a variety of naming and directory services to be plugged in transparently, thereby allowing the Java application using the JNDI API to access their services. See the following figure.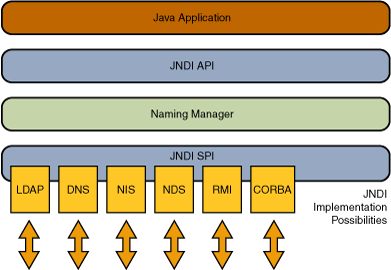
Packaging
JNDI is included in the Java SE Platform. To use the JNDI, you must have the JNDI classes and one or more service providers. The JDK includes service providers for the following naming/directory services:- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
- Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) Common Object Services (COS) name service
- Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Registry
- Domain Name Service (DNS)
Other service providers can be downloaded from the JNDI Web site or obtained from other vendors.
The JNDI is divided into five packages:
The next part of the lesson has a brief description of the JNDI packages.