Document Object Model APIs
Figure 1-2 shows the DOM APIs in action.
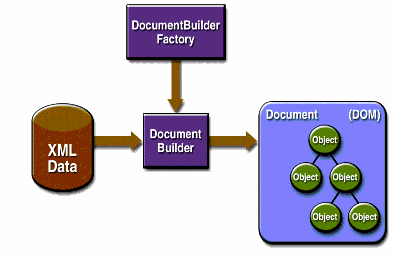
You use the javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory class to get a DocumentBuilder instance, and you use that instance to produce a Document object that conforms to the DOM specification. The builder you get, in fact, is determined by the system property javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory, which selects the factory implementation that is used to produce the builder. (The platform's default value can be overridden from the command line.)
You can also use the DocumentBuilder newDocument() method to create an empty Document that implements the org.w3c.dom.Document interface. Alternatively, you can use one of the builder's parse methods to create a Document from existing XML data. The result is a DOM tree like that shown in Figure 1-2.
Note - Although they are called objects, the entries in the DOM tree are actually fairly low-level data structures. For example, consider this structure: <color>blue</color>. There is an element node for the color tag, and under that there is a text node that contains the data, blue! This issue will be explored at length in the DOM lesson of this tutorial, but developers who are expecting objects are usually surprised to find that invoking getNodeValue() on the element node returns nothing. For a truly object-oriented tree, see the JDOM API at http://www.jdom.org .
DOM Packages
The Document Object Model implementation is defined in the packages listed in Table 1-2.
Table 1-2 DOM Packages
Package |
Description |
|---|---|
org.w3c.dom |
Defines the DOM programming interfaces for XML (and, optionally, HTML) documents, as specified by the W3C. |
javax.xml.parsers |
Defines the DocumentBuilderFactory class and the DocumentBuilder class, which returns an object that implements the W3C Document interface. The factory that is used to create the builder is determined by the javax.xml.parsers system property, which can be set from the command line or overridden when invoking the new Instance method. This package also defines the ParserConfigurationException class for reporting errors. |
