Bound Properties
Bound properties support the
PropertyChangeListener (in the API reference
documentation) class.
Sometimes when a Bean property changes, another object
might need to be
notified of the change, and react to the change.
Whenever a bound property changes, notification of the change is sent to interested listeners.
The accessor methods for a bound property are defined in the same way as
those for simple properties. However, you also need to provide the event
listener registration methods forPropertyChangeListener
classes and fire a
PropertyChangeEvent (in the API reference documentation) event to the PropertyChangeListener objects by
calling their propertyChange methods
The convenience
PropertyChangeSupport (in the API reference documentation) class enables your bean to implement these methods.
Your bean can inherit changes from
the PropertyChangeSupportclass,
or use it as an inner class.
In order to listen for property changes, an object must be able to add and remove itself from the listener list on the bean containing the bound property. It must also be able to respond to the event notification method that signals a property change.
The PropertyChangeEvent class encapsulates property change information, and
is sent from the property change event source to each object in the property
change listener list with the
propertyChange method.
Implementing Bound Property Support Within a Bean
To implement a bound property in your application, follow these steps:- Import the
java.beanspackage. This gives you access to thePropertyChangeSupportclass. - Instantiate a
PropertyChangeSupportobject. This object maintains the property change listener list and fires property change events. You can also make your class aPropertyChangeSupportsubclass. - Implement methods to maintain the property change listener list.
Since a
PropertyChangeSupportsubclass implements these methods, you merely wrap calls to the property-change support object's methods. - Modify a property's set method to fire a property change event when the property is changed.
Creating a Bound Property
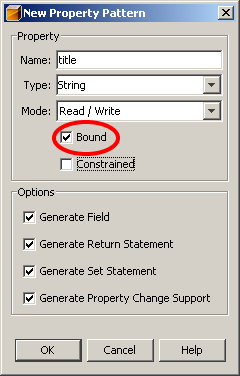
To create the title property as a bound property for the MyBean component in the NetBeans GUI Builder, perform the following sequence of operations:- Right-click the Bean Patterns node in the
MyBeanclass hierarchy. - Select Add|Property from the pop-up menu.
- Fill the New Property Pattern form as shown on the following figure
and click OK.
- Note that the title property and the multicast event source pattern
PropertyChangeListenerwere added to the Bean Patterns structure.
You can also modify existing code generated in the previous lesson to convert the title and lines properties to the bound type as follows (where newly added code is shown in bold):
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.beans.PropertyChangeListener;
import java.beans.PropertyChangeSupport;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.swing.JComponent;
/**
* Bean with bound properties.
*/
public class MyBean
extends JComponent
implements Serializable
{
private String title;
private String[] lines = new String[10];
private final PropertyChangeSupport pcs = new PropertyChangeSupport( this );
public String getTitle()
{
return this.title;
}
public void setTitle( String title )
{
String old = this.title;
this.title = title;
this.pcs.firePropertyChange( "title", old, title );
}
public String[] getLines()
{
return this.lines.clone();
}
public String getLines( int index )
{
return this.lines[index];
}
public void setLines( String[] lines )
{
String[] old = this.lines;
this.lines = lines;
this.pcs.firePropertyChange( "lines", old, lines );
}
public void setLines( int index, String line )
{
String old = this.lines[index];
this.lines[index] = line;
this.pcs.fireIndexedPropertyChange( "lines", index, old, lines );
}
public void addPropertyChangeListener( PropertyChangeListener listener )
{
this.pcs.addPropertyChangeListener( listener );
}
public void removePropertyChangeListener( PropertyChangeListener listener )
{
this.pcs.removePropertyChangeListener( listener );
}
protected void paintComponent( Graphics g )
{
g.setColor( getForeground() );
int height = g.getFontMetrics().getHeight();
paintString( g, this.title, height );
if ( this.lines != null )
{
int step = height;
for ( String line : this.lines )
paintString( g, line, height += step );
}
}
private void paintString( Graphics g, String str, int height )
{
if ( str != null )
g.drawString( str, 0, height );
}
}
